How much do you know about the Export Logistics Consolidation Warehouse? With the rapid growth of cross-border e-commerce, sellers have high demands for storage and logistics efficiency. In China, export forward warehouses for cross-border e-commerce have been developing quickly in the past couple of years. So, what exactly are these warehouses?
General knowledge of consolidation warehouses
For cross-border E-commerce sellers, the consolidation warehouses are typically located close to the final sales city or the origin city of goods. More closed, higher efficiency – That’s the overall idea for the rapidly running E-commerce businesses all over the world.
Actually, consolidation warehouse is not a new business. Earlier in the past dozens of years, it has been developed to be a very mature business in The US.
Off-site Logistics Consolidation Warehouse In Traditional Supply Chain
There are a lot of huge supermarkets and corresponding distribution centers in the USA. Hence, consolidation warehouses were very mature there. They are very important existence in the developed countries. However, nowadays we still need to realize that the cross-border e-commerce export logistics consolidation warehouse is very different. Different rules in the origin country and importing country are very different, more or less. Moreover, “smart” is a distinguishing feature of modern e-commerce warehousing with strong IT support.
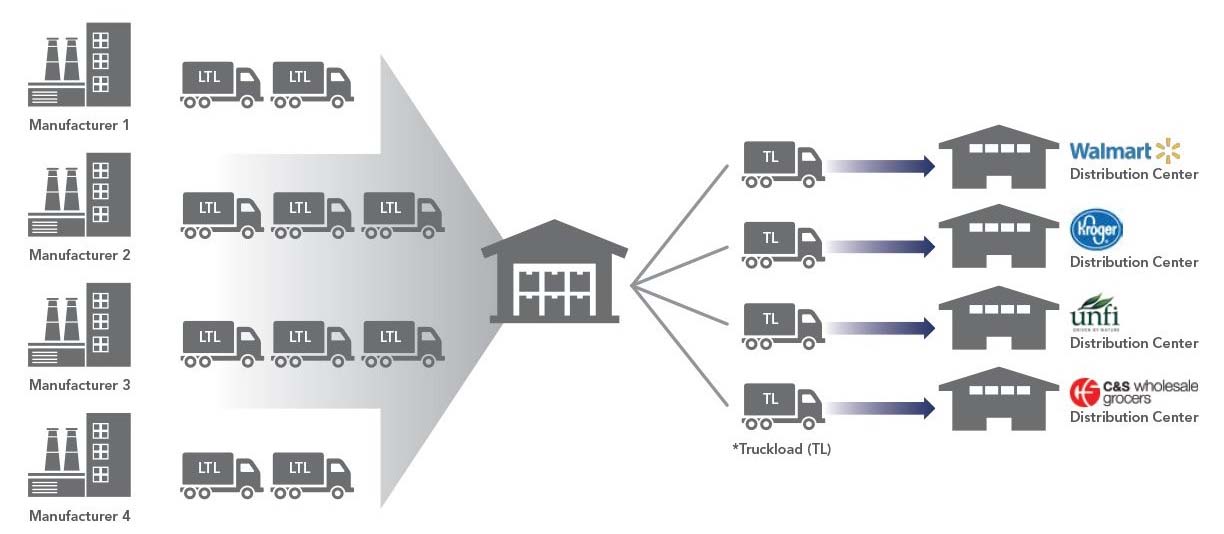
In traditional consolidation warehousing, multiple LTL orders are sent shorter (cheaper) distances to the central consolidation center. Remaining distance to distribution center discounted at full truckload price, consolidated with other customers.
Cross-border logistics consolidation warehouse
Basically, there are two types of cross-border e-commerce consolidation warehouses: Export consolidation warehouses and sales consolidation warehouses in the importing countries.
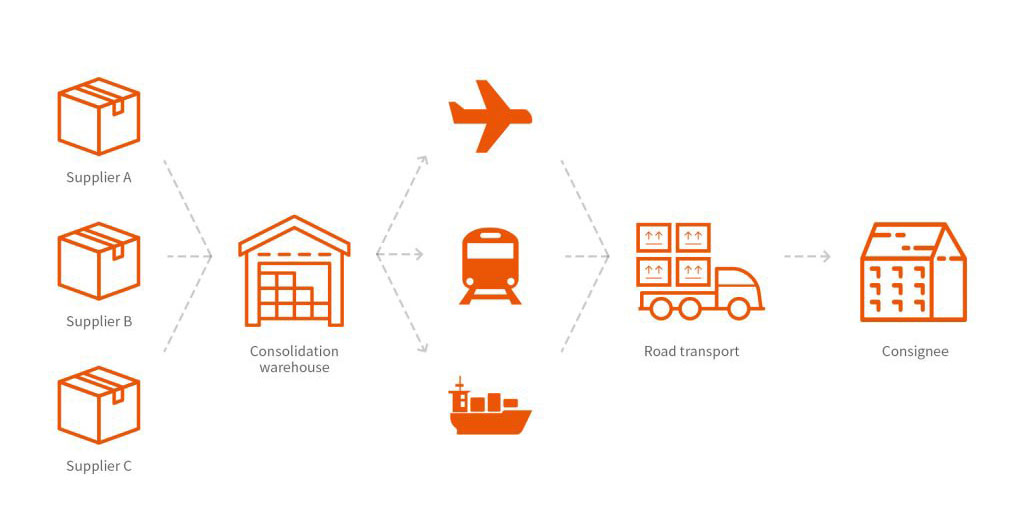
These warehouses significantly improve the “last mile” delivery efficiency for both exports and imports. They are an innovative solution for cross-border e-commerce logistics, refining traditional logistics processes.
If you’re a cross-border e-commerce seller or buyer, you might now understand the difference between forward warehouses and overseas warehouses. Forward warehouses are closer to the source or sales area but are generally smaller in size than overseas warehouses.
The concept of sales forward warehouses near the source or sales area is straightforward. This article focuses on China’s cross-border e-commerce export logistics consolidation warehouse.
Shipping Services From China
Inquire us for cross-border shipping solutions
The export logistics consolidation warehouse is set up at a domestic port, serving as logistics center for cross-border e-commerce exports
Simplify the customs inspection procedure
In an export logistics consolidation warehouse, we can offer storage, customs clearance, cargo consolidation and inspection.
Before, exports is under the traditional “shipping out” model. Need to arrange consolidation, customs clearance and entering the port area.
But e-commerce exports is much different. They are more diverse, smaller and more frequent. Many packages are consolidated into one container. That brings much more possibility of customs inspection. It’s also a big trouble to make post-inspection and repacking. Frankly speaking, as an international shipping forwarder, in the past years, Quicker has seen and went through too much shipment delay caused by post-inspection and repacking.
Export logistics consolidation warehouse do changed a lot of things! Big improvement. In the new procedure, the inspection is before shipping. Goods can be cleared as individual items in the warehouse and then consolidated. That reduces customs clearance time from 2-3 days to about 1 day.

Specifically, three benefits to e-commerce business
Compliance, efficiency and cost reduction.
Shipping companies can achieve same-day inspection and shipping. It means a at least 30% higer of logistics efficiency. It also means reducing costs by 20%. They totally optimize the modern supply chains – More precisely and respond flexibly to risks. Really very huge changes! Looking at those rich cross-bording e-commerce companies and you will know why they can make big money each day in a “silence” status, in their office.
Export forward warehouses allow sellers to store products in China, avoiding complex cross-border logistics like relabeling, repackaging, and customs procedures. Goods still need customs clearance in China, but sending them to the forward warehouse completes this process.
These warehouses also enhance product quality and user experience by conducting quality checks and packaging, ensuring products meet import standards and improving brand image.
In summary, China’s cross-border e-commerce export logistics consolidation warehouse significantly enhance storage and logistics efficiency for sellers both domestically and internationally.
Key locations of those export logistics consolidation warehouse in China
China’s cross-border e-commerce export logistics warehouses are strategically located in regions that serve as major hubs for manufacturing, trade, and international shipping. These locations are carefully chosen to optimize access to suppliers, transportation networks, and international markets, enabling efficient operations and faster delivery times for global customers.

One of the most prominent regions for these warehouses is the Pearl River Delta, which includes cities like Shenzhen and Guangzhou. Shenzhen, often referred to as the “Silicon Valley of Hardware,” is a global manufacturing powerhouse and home to countless factories producing electronics, consumer goods, and other export products. The proximity of warehouses to these manufacturing sites allows businesses to consolidate goods quickly and at lower costs. Additionally, Shenzhen’s well-developed logistics infrastructure, including its international airport and port, facilitates the smooth movement of goods to destinations worldwide. Guangzhou, another key city in this region, complements Shenzhen with its strong focus on traditional manufacturing and its role as a major trading hub.
Moving northward, Yiwu in Zhejiang Province is another critical location for cross-border e-commerce warehouses. Known as the world’s largest wholesale market for small commodities, Yiwu is a hotspot for sourcing affordable goods like fashion accessories, home decor, and toys. Many cross-border sellers choose to base their operations here because of the sheer variety of products available and the cost advantages. Warehouses in Yiwu are closely integrated with suppliers, enabling rapid order fulfillment and shipment for international buyers.
Shanghai, as China’s largest city and one of the world’s busiest ports, is another key location for these warehouses. Shanghai’s role as a global financial and shipping hub makes it an ideal choice for businesses targeting high-volume exports. The city’s advanced infrastructure, including its deep-water port and Pudong International Airport, ensures smooth connectivity to international markets. Additionally, Shanghai’s position as a center for innovation and technology has led to the adoption of advanced warehouse automation systems, further enhancing operational efficiency.
In northern China, Tianjin and Beijing also play important roles. Tianjin, with its large port facilities, serves as a gateway for goods destined for markets in Europe, the Middle East, and beyond. Meanwhile, Beijing, as the political and economic center of China, is home to warehouses that cater to cross-border businesses looking to leverage the city’s robust logistics networks and access to government resources.
Other emerging locations include Hangzhou, the headquarters of Alibaba, which has become a hub for e-commerce innovation and logistics development, and Chengdu, which is gaining prominence due to its strategic position in western China and its growing role in connecting inland regions with global markets.
In summary, the key locations of cross-border e-commerce export logistics consolidation warehouse in China – such as Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Yiwu, Shanghai, and Tianjin – are strategically chosen to leverage regional strengths in manufacturing, trade, and logistics. These hubs not only facilitate faster and more cost-effective shipping but also enable businesses to scale their operations globally with greater efficiency.
What’s the challenges for widely use export logisitcs consolidation warehouse?
More or less, we have admit that super fast speed and extreme convenience in logistics will cause cost up. Obviously, the investment on high-tech devices and IT system are very expensive. However, in the other hand, the average logistics cost sharing on single product is much lower before because of much higher transport efficency.
Cross-border e-commerce logistics is a dynamic and fast-growing industry, but it comes with its own set of challenges. These challenges can impact operational efficiency, profitability and customer satisfaction if not managed effectively. Below are some of the key obstacles faced by businesses in this sector:
Shipping From China
Quicker International Logistics
Customs regulations
Navigating customs regulations is one of the most significant challenges in cross-border e-commerce logistics consolidation warehouse. Each country has its own set of rules, documentation requirements and tariff systems. For example:
Strict Export and Import Regulations. Businesses must comply with various export and import laws, including product classifications, packaging standards and labeling requirements. Failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to shipment delays, penalties, or even confiscation of goods.
Documentation and Compliance. Accurate documentation, such as commercial invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, is essential for smooth customs clearance. Errors or missing paperwork can result in additional scrutiny or rejection of shipments.
Changing Trade Policies. Trade agreements, tariffs and restrictions can change frequently due to geopolitical factors, creating uncertainty and requiring businesses to stay updated and adapt quickly.
Customs Delays: Even when all regulations are followed, customs inspections can cause delays, especially during peak seasons or in countries with less efficient customs processes.
Rising logistics costs
The cost of logistics is a critical factor in cross-border e-commerce, and rising expenses can erode profitability. Key cost-related challenges include:
Fluctuating shipping rates. Air and sea freight rates are highly volatile and can be influenced by factors such as fuel prices, seasonal demand, capacity shortages, and global disruptions (e.g., pandemics or geopolitical conflicts). Sudden price spikes can strain small and medium-sized businesses.
Warehousing costs. As demand for cross-border e-commerce grows, the cost of renting or operating warehouses—especially in high-demand areas like Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Shanghai—continues to rise.
Last-mile delivery costs. Delivering goods to the end customer, particularly in remote or rural areas, is often the most expensive part of the logistics chain. These costs can escalate further in countries with underdeveloped delivery infrastructure.
Surcharges and fees. Additional charges, such as fuel surcharges, peak season fees and customs brokerage fees, can add to the overall logistics expenses.
Inventory management
Managing inventory effectively is a complex task to logistics consolidation warehouse, particularly for businesses operating across multiple platforms and markets. Key challenges include:
Stock coordination across platforms. Many cross-border e-commerce sellers operate on multiple platforms, such as Amazon, eBay, and Shopify, as well as regional marketplaces like Lazada or AliExpress. Keeping track of stock levels, updating inventory in real time, and avoiding overselling or stockouts can be difficult.
Demand forecasting. Predicting demand in different markets is challenging due to cultural differences, seasonal trends, and changing consumer preferences. Overestimating demand can lead to excess inventory and storage costs, while underestimating it can result in missed sales opportunities.
Returns management. Handling international returns is particularly complicated, as it involves reverse logistics, additional shipping costs, and potential customs issues. Poorly managed returns can lead to customer dissatisfaction and increased expenses.
Global delivery issues
Ensuring timely and reliable delivery to customers in different countries presents unique challenges, particularly in the “last mile” of the logistics process. Common issues include:
Last-mile delivery challenges. Delivering goods in the destination country often involves navigating local infrastructure, which may be underdeveloped in some regions. For example, rural areas may lack reliable delivery services, while urban areas may face congestion and delivery restrictions.
Customs delays at destination. Even after goods clear export customs in China, they may face delays at the destination country’s customs if there are discrepancies in documentation or if the goods are flagged for inspection.
Local carrier reliability. In many cases, cross-border shipments are handed over to local carriers for final delivery. The quality and reliability of these carriers can vary significantly, leading to inconsistent delivery times and customer dissatisfaction.
Address and language barriers. Inaccurate or incomplete delivery addresses, as well as language differences, can cause delivery failures or delays. This is particularly common in regions with complex addressing systems or non-Latin alphabets.
Customer expectations. With the rise of platforms like Amazon offering fast delivery options, customers now expect quicker shipping times, even for international orders. Meeting these expectations while managing costs is a constant balancing act for businesses.
Trends in cross-border e-commerce warehousing
As cross-border e-commerce continues to grow, the warehousing and logistics sector is evolving rapidly to meet the increasing demands for efficiency, speed, and sustainability. Several key trends are shaping the future of cross-border e-commerce warehousing, driven by advancements in technology, changes in consumer expectations, and global market dynamics.
Automation and technology
Automation and advanced technologies are transforming the way warehouses operate, making processes faster, more accurate, and cost-efficient. Some of the most impactful innovations include:



AI is being used to optimize warehouse operations by improving demand forecasting, inventory management, and order picking. AI-powered algorithms can analyze historical sales data and predict future demand, ensuring that warehouses are stocked with the right products at the right time.
Robots are increasingly being deployed in warehouses to handle repetitive tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting. For example, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can navigate warehouse floors, retrieve items, and transport them to packing stations, significantly reducing human labor and increasing efficiency.
IoT devices, such as smart sensors and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, are being used to track inventory in real time. These technologies provide warehouse managers with greater visibility into stock levels, item locations, and shipment statuses, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall efficiency.
Blockchain technology is being adopted to enhance transparency and traceability in cross-border e-commerce logistics. By creating a secure and immutable record of transactions, blockchain ensures that all parties in the supply chain—manufacturers, warehouses, logistics providers, and customers—can track the movement of goods with confidence. This is particularly important for high-value or sensitive items, such as electronics or pharmaceuticals.
Bonded warehouses
The use of bonded warehouses is becoming increasingly popular in cross-border e-commerce, offering significant advantages for businesses:
What are bonded warehouses? Bonded warehouses are special facilities where goods can be stored without immediate payment of import duties or taxes. These goods remain in the warehouse until they are sold and shipped to their final destination, at which point the applicable taxes are paid.
Benefits for cross-border e-commerce. Bonded warehouses allow businesses to reduce upfront costs by deferring tax payments. This is especially beneficial for sellers dealing with high-value or bulk goods. Additionally, bonded warehouses simplify customs clearance processes, as goods are pre-checked and stored in a controlled environment, reducing the risk of delays.
Growth in bonded warehouses. In China, cities like Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Shanghai are seeing a rapid expansion of bonded warehouse facilities, driven by government support for cross-border trade. These warehouses are strategically located near ports and airports to facilitate quick and efficient shipping.
Green logistics
Sustainability is becoming a key focus in the cross-border e-commerce warehousing and logistics industry, as businesses and consumers alike prioritize environmental responsibility. Key developments include:
Eco-friendly packaging. Warehouses are adopting sustainable packaging solutions, such as biodegradable materials, recyclable boxes, and reusable packaging. This not only reduces waste but also aligns with consumer preferences for environmentally friendly practices.
Carbon-neutral shipping. Many e-commerce companies are working to offset their carbon emissions by investing in renewable energy projects or purchasing carbon credits. Warehouses play a role in this by optimizing transportation routes, consolidating shipments, and using energy-efficient equipment.
Energy-efficient warehouses. Modern warehouses are being designed to minimize their environmental impact. Features such as solar panels, LED lighting, and advanced climate control systems help reduce energy consumption, while automated systems ensure that resources are used efficiently.
Global expansion
To better serve international markets, Chinese cross-border e-commerce companies are increasingly investing in overseas warehouses. This trend is reshaping the global logistics landscape and offering new opportunities for businesses:
Why overseas warehouses? Overseas warehouses allow businesses to store inventory closer to their customers, enabling faster delivery times and improved customer satisfaction. By pre-positioning goods in key markets, companies can also reduce shipping costs and avoid customs delays.
Key destinations for expansion. Chinese companies are setting up warehouses in strategic locations such as the United States, Europe, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East. For example, Cainiao (Alibaba’s logistics arm) and JD Logistics have established extensive networks of overseas warehouses to support their global operations.
Impact on customer experience. Overseas warehouses enable e-commerce businesses to offer services such as same-day or next-day delivery, which are increasingly expected by international customers. They also make it easier to handle returns, as goods can be processed locally rather than being shipped back to China.
Challenges of global expansion. While overseas warehouses offer many benefits, they also come with challenges, such as higher operational costs, local regulatory compliance, and the need to manage multiple supply chains effectively.
That’s a deep knowledge about the export logistics consolidation warehouse in China. Hope to help you from China. Just consult us for free. Save the logistics fee shipping from China with Quicker International Logistics (Shenzhen).